Muscular System of Humans
Muscular System of Humans: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Skeletal Muscle, Sarcomere, Muscle Contraction, Mechanism of Muscle Contraction, Troponin, Myoglobin, Myofibril, Myosin, Actin, Muscle Fibre, Contractile Proteins, Tropomyosin and, Muscular System in Human
Important Questions on Muscular System of Humans
Which protein is present in muscles?
Monomeric G-actin polymerises to form __A___ in the presence of Mg++ ions. Select the correct option that correctly identifies A.
Arrange the following order of events taking place during muscle contraction in correct order.
a. Nerve impulse
b. Cross-bridge formation
c. Release of calcium ions
d. Impulse reaches sarcoplasmic reticulum
e. Actin - Myosin complex
f. Muscle contraction
Which option is correct among the following statements related to muscle fibre ?
1) Binding of calcium with a subunit of troponin (TnC) removes the masking of active sites for myosin.
2) Pumping of calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic cisternae results in masking of active sites on the actin.
Anatomical unit of muscle is –
Which of the following is not a correct difference between white and red muscles fibre?
| White muscle fibre | Red muscle fibre | ||
| 1. | Less myoglobin | 1. |
More myoglobin |
| 2. | Number of mitochondria is less. | 2. |
Number of mitochondria is more. |
| 3. | Amount of sarcoplasmic reticulum is low. |
3. |
Amount of sarcoplasmic reticulum is high. |
| 4. | Aerobic muscle | 4. | Anaerobic muscle |
A neurotransmitter _____ generates an action potential in the sarcolemma.
Go through the following diagram describing muscle contraction. Identify the parts from A to D.
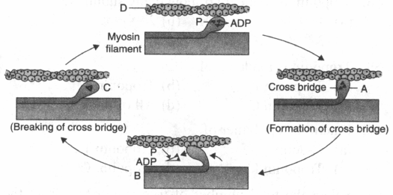
Arrange the following statements in correct sequence to describe muscle contraction.
1. Signal sent by CNS through motor neuron.
2. Generation of action potential in the sarcolemma.
3. Release of from sarcoplasmic reticulum.
4. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is released from motor end plate.
5. Sarcomere is shortened.
According to the sliding filament theory,
A motor unit is best described as
ATP provides energy for muscle contraction by allowing for
Identify A to D in the below figure.
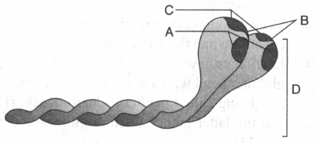
Following is the figure of actin (thin) filaments. Identify the parts A, B and C in the given diagram.

Binding of with _____ in the skeletal muscles which leads to exposure of the binding site for _____ on the filament _____.
Select the total number of true statements from the following?
1. Each myosin (thick) filament is also a polymerized protein.
2. Many monomeric proteins called meromyosins constitute one thick filament.
3. Each meromyosin has two important parts, a globular head with a short arm and a tail, the former being called the heavy meromyosin (HMM) and the latter being called the light meromyosin (LMM).
4. The HMM component, i.e., the head and short arm projects outwards at regular distance and angle from each other from the surface of a polymerized myosin filament and it is known as cross arm.
5. The globular head is an active ATPase enzyme and has binding sites for ATP and active sites for actin.
Troponin is made up of how many subunits?
Which of the following masks the binding active site for myosin on the actin filament?
Globular head of myosin contains binding site for
